
Overview of Parylene Coating
Parylene: An organic material in the form of a colorless, transparent thermoplastic polymer, which, in powder form, undergoes polymerization in a vacuum state to form a thin film on the surface of the target object.
Commercialization of Parylene: 1990s
Gaining attention as a uniform coating technology that provides protective layers on surfaces for various components, electronics, telecommunications, mechanical parts, and medical devices, offering insulation, corrosion resistance, waterproofing, and prevention of powder scattering.
Since it is vapor-deposited in a vacuum state, it can solve problems such as deformation and surface shrinkage caused by solution-process coatings and drying. Moreover, due to surface polymerization in a gaseous state, it enables uniform coating even in fine molds and structures.
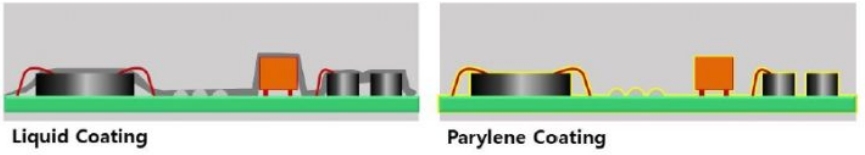
Parylene coating is a method that uses parylene, a polymer material, to form a thin and uniform protective layer. This coating is achieved through a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process in a vacuum state and can be applied to various materials such as electronic components, medical devices, metals, and plastics. The key characteristics of parylene coating include high insulation, moisture resistance, chemical resistance, and uniform thickness, which protect products from external environments and significantly enhance their durability.
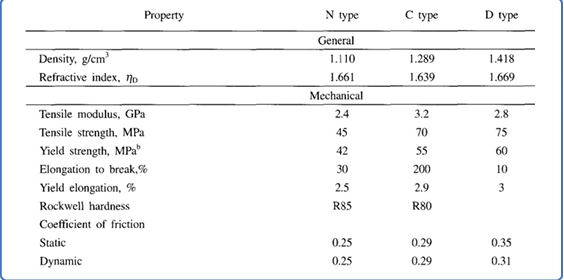
The mechanical properties of parylene polymer films are similar to those of conventional plastics.
Generally, an increase in crystallinity due to aging or heat treatment decreases elongation at break while increasing modulus and strength.
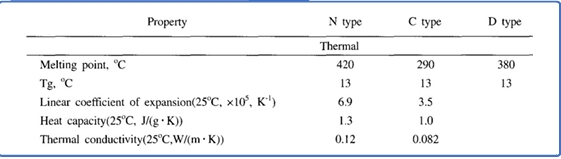
- When parylene films are exposed in an oven circulating air at a constant temperature:
- The failure criterion is defined as a 50% reduction in tensile strength. Parylene types N, C, and D maintain their physical properties without changes at 60°C, 80°C, and 100°C, respectively, for 10 years in atmospheric conditions.
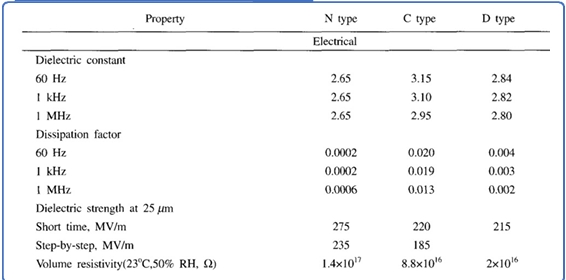
- The electrical properties of parylene are excellent for use in low-power devices: Low dielectric constant and dielectric loss.
- Unaffected by water absorption at room temperature.
- Dielectric strength is relatively high.
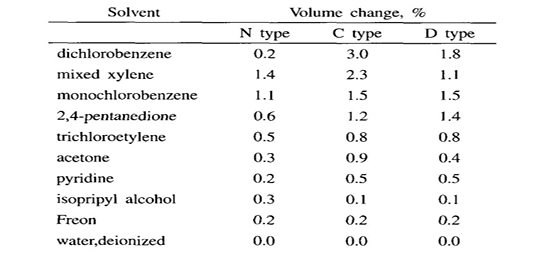
- Below the melting point of crystalline polymers, parylene exhibits resistance to all existing solvents.
- When parylene film is exposed to organic solvents, slight swelling occurs as the solvent penetrates the amorphous phase.
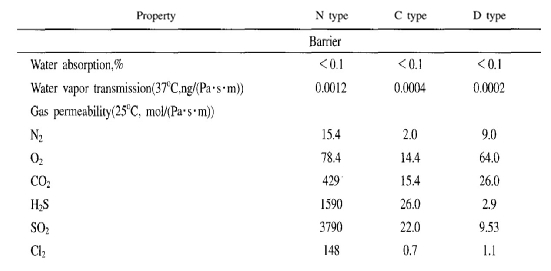
- Radiation Resistance, Optics, and Surface Characteristics
- The surface condition of deposited materials remains unchanged, ensuring consistent deposition.
- Among organic polymer coatings, parylene exhibits excellent radiation resistance.
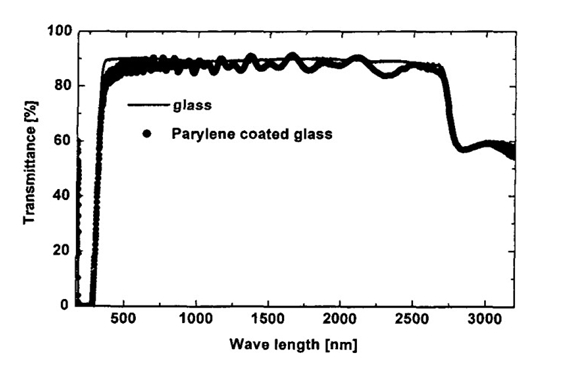
- Thin films and coatings are transparent in the visible light range but opaque under ultraviolet light.
- UV/VIS measurements of glass before and after parylene coating confirm a light transmittance of over 90%.
Parylene Coating Equipment

Small-Scale Equipment
[엠바디텍]

Medium-Scale Equipment
[엠바디텍]

Large-Scale Equipment
[엠바디텍]

Custom Design Requests Available
[엠바디텍]
Applications of Parylene Coating
Semiconductor
Probes/PCBs/Load Boards

Electronics
Electronic devices, aviation equipment, mechanical devices, etc.
Medical Field
Medical devices, surgical instruments, medical needles, etc.

LCD/OLED
LCD lamps, LCD panels, OLED products, etc.
